Last year saw the explosion of Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI), a new mainstream technology kick started by the launch of ChatGPT to the general public at the end of November 2022.
Within months, major tech companies like Google and Microsoft, along with a raft of start-ups, had followed suit with rival chatbots. Their impact was immediate, with Reuters noting that “the generative AI craze has disrupted several industries from cloud computing and customer service to movie editing and screenplay writing.”
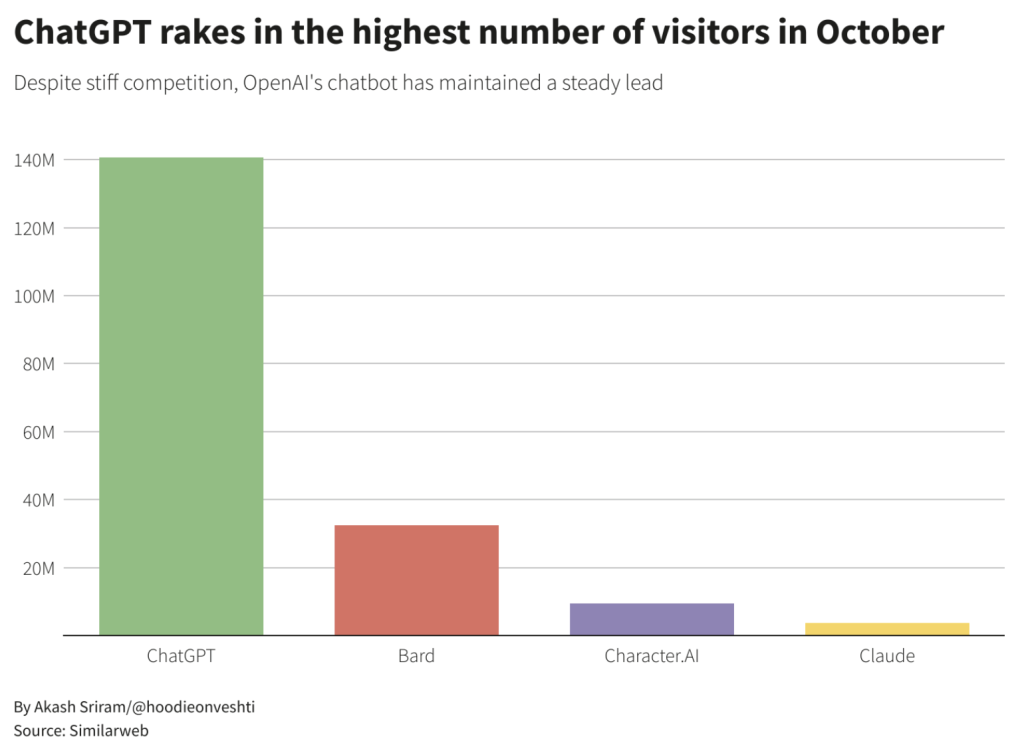
Within this, the market leader, ChatGPT, reached 1 million users in just five days after its launch. That had grown to 140 million users a month – and 100 million a week – by its first birthday, demonstrating how quickly this technology had been adopted in some circles, including more than 92% of Fortune 500 companies.
But what is Generative AI? What does it do? And why should you care about it?
After all, plenty of technologies – from virtual reality to cryptocurrency and 3D – have been hugely hyped among the Technorati. Many of these have failed to go mainstream, or have briefly had their moment in the sun and then fizzled out.
This article aims to demystify the concept of Generative AI and shed light on why it matters.
Given its potential significance, it’s a topic we’ll explore in more detail in the next issue too, diving into how you can use it, and the implications for you and your business.
What is Generative AI?
This cutting-edge technology has the potential to revolutionize numerous industries, through an ability to create new and original content, such as text, images, music, and more, based on the prompts provided by its users.
Want to write a speech for a wedding? Input a few details about the bride and groom and let your AI tool do the rest. (I did this, and the proposed speech was pretty good. The AI generated this in seconds. It would have taken me hours.)
Looking to brainstorm ideas for a trip to Hawaii? Your AI can help with that and even come up with a recommended itinerary for you. It can even put together a New Year workout schedule so that you’re beach fit in time for Spring Break.
And how about creating an image in the style of Salvador Dali of a cow jumping over the moon, or a refresh of your company logo? There are AI tools that can design those for you too.

How it works
To do this, Generative AI programs rely on prompts from users. The better and more specific the guidance, the greater the likelihood of a useful response.
Doing this requires no coding or specific technical know-how by users. Just detailed prompts about what you are looking for. More often than not, that may involve some trial and error too.
To inform these responses, Generative AI programs have been trained on huge datasets, ingesting and processing this material to look for patterns and links between information.
From that knowledge base, Generative AI programs can then remix this to autonomously create new content. That means programs are only as good as the material they’ve been trained on as well as the prompts that are entered into them. As such, it’s important to recognize that Generative AI models can also inherit biases present in the data they are trained on.
Furthermore, one common challenge for many users of these tools is that AI programs are inclined to “hallucinate.” These are responses generated by an AI that include false or made-up information. Dictionary.com picked “hallucinate” as its word of the year at the end of 2023.
Nevertheless, when done well, it can be hard to discern between ideas and output produced by a machine and those created by a human. And, in some cases, the lines are increasingly hazy, such as with the creative work – including art, music, literature and speculative architecture- produced by AI artists.
In short Generative AI is rapidly blurring the lines between human and machine creativity. And while that may sound like Science Fiction arguably it’s just the latest stage in a long-running technological evolution. From ‘Deep Blue’ defeated chess grandmaster Garry Kasparov, to
IBM’s Watson winning Jeopardy and the emergence of self-driving cars, the growing capabilities of machines have long been telegraphed.
What is the impact of all this?
This is either exciting or terrifying, depending on which side of the fence you sit.
For enthusiasts, it will unlock solutions to issues in fields like medicine and enable us to tackle climate change, while others highlight potential benefits in terms of productivity, the creation of new products, improved customer service and countless other use cases.
At the same time, there are fears about our ability to reign in “rogue” AI actors, a notion that may seem right out of a Hollywood movie, but is not without justification.
Meanwhile, the ability to use AI to automate tasks, or produce creative work, means that journalists have been writing for some time about how “robots are coming for your jobs.”
Alongside this, the ability to generate convincing fake content raises legitimate concerns about misinformation and malicious use. That’s especially concerning in an election year.
Coupled with the fact that these programs also have a habit of filling in the gaps and making things up, then it’s clear that ensuring accuracy, fairness and reducing bias, will remain ongoing challenges for this technology.
To offset these issues, stricter regulations and responsible AI development are crucial to mitigate these risks. Policy makers are looking at this, even if they are struggling to keep up with the pace of change.

Moving Forward
Generative AI’s momentum appears unstoppable as tech firms and developers look to unlock its full creative possibilities.
A lot of initial coverage about this technology focused on its impact in areas such as education, with concerns that students would use Generative AI to cheat on exams or do their homework. That remains a legitimate concern, but the potential of this technology is much deeper and richer than that.
As we’ll see in the next issue, businesses across a wide range of different industries are also embracing Generative AI. They’re experimenting with these tools as a means to foster creativity and innovation, efficiency and automation, as well as developing new products and workflows.
The ability of Generative AI to disrupt and change so much of what we do and how we do it, means that embracing and understanding Generative AI is essential. Failure to do so will make it difficult for individuals and organizations to thrive in the modern economy.
This technology is not foolproof, reflecting perhaps how nascent much of it is. However, despite its flaws, Generative AI offers us our first glimpse into a future where machines and humans can easily collaborate to solve problems and create content.
In this brave new world, Generative AI can add real value, but human oversight remains important. That means it is essential for users to be able to critically evaluate the content and results that Generative AI programs create.
The machines are coming, but they’re not going to be taking over from us just yet.









